Answer 1. Two important decision making points:
Q 2. What Happens During Knee Replacement Surgery?
Answer 2. The damaged part of the knee joint is removed from the surface of the bones, and the surfaces are then shaped to hold a metal/plastic artificial joint. The artificial joint is attached to the thigh bone, shin and knee cap either with bone cement or a special material. When fit together, the attached artificial parts form the joint, relying on the surrounding muscles and ligaments for support and function
Q 3. What Happens After Knee Replacement Surgery?
1. How many days I need to stay at hospital?
# The average hospital stay after knee joint replacement is usually three to five days
2.When will I start walking again after my knee replacement?
# You start walking from very next day of your surgery. After knee joint replacement, the patient are standing and moving the joint the day after surgery. At first, you may walk with the help of support — such as walker, or cane — will be used until your knee is able to support your full body weight. After about six weeks, most people are walking comfortably with minimal assistance. Once muscle strength is restored with physical therapy, people who have had knee joint replacement surgery can enjoy most activities.
4. How Long Will I Need Physical Therapy After Knee Replacement?
Answer 4. Sessions with your physical therapist usually last for 1 month post surgery. After knee replacement surgery, you are usually sent home and your doctor will usually have a physical therapist come to treat you at home. Remember, every person is different and the course of rehabilitation will be determined on an individual basis with the assistance of your doctor and physical therapist. Physiotherapy is one the most important independent factor responsible for good outcome of your knee replacement.
Q 5.Common questions asked by patients regarding recovery period is:
1. When will I start walking?
# Usually from next day of your surgery
2. When will I be going to washroom independently?
Within 3 to 4 days of your surgery. You usually go to the toilet independently at home with your knee braces applied and using some aid for ambulation e.g. walker.
3.How long the pain will last?
# Every patient is different. Usually patients has significant pain relieve within 3 to 6 weeks post surgery.
4. When will I be able to resume my office?
# Usually after 4 to 6 weeks of your surgery.
5. When to start driving?
# Car driving can be started between 6 -8 weeks and scooter or bike can be started after 3 -4 months of your surgery.
6. How long my knee swelling will be their?
# After knee replacement swelling is not uncommon. Mild swelling may last for even 6 to 9 month.
Q6. I am really afraid of knee replacement, will it be successful?
Answer 6. A major reason for putting off a hip or knee replacement replacement can be summed up in one word: fear. Fear of the unknown. Fear of pain. Fear of recovery. Fear of being vulnerable. Their are around 1.5 lacs knee replacement surgeries are done in India every year and around 6 lacs done in US.
Q7. Is Baghwan Mahavir Medica Superspeciality Hospital, Ranchi, a safe place to go for Joint Replacement Surgeries?
Answer 6. YES. Medica Institute of Orthopaedics has dedicate wing of JOINT REPLACEMENT with highlyqualified doctors for Joint/knee replacement, headed by Dr. Ankur Saurav who has many laureates in the field of Joint Replacement and has worked and received his fellowship in Joint Replacement from Munich, Germany. Medica hospital,Ranchi is equipped with a state-of-the-art Digital Orthopaedics Operating Theatre. Joint Replacement unit is well supported by strong Anaesthesia team/Critical Care backup, Physiotherapy team, well trained nurses and dedicated staff.
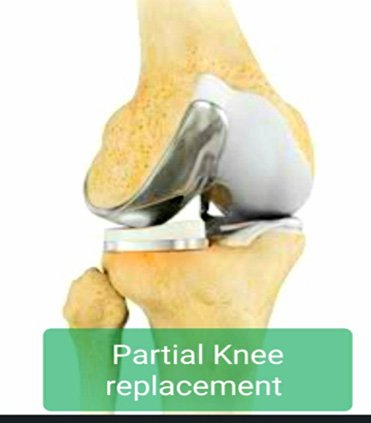
Now world is moving fast in Joint Replacement and specially Knee Replacement. From no Replacement to Total Knee Replacement with lots of restrictions to High mobility Knee Replacement with long durable knees. Now we are thinking of preserving ones

knee natural structures, with minimally invasive surgery and providing pain relief at the same time with shorter Rehabilitation and Physiotherapy. Partial or Uni knee Replacement is a strong step towards it.
Partial knee replacement is a type of knee replacement where we only change the diseased part of knee and rest of the knee is left untouched and also the four main ligaments which supports the knee is left intact(where as in total knee replacement two out of four ligament is removed while surgery). Uni/Partial knee replacement has one major limitation that it can't be done in patients having more than one half of the knee damaged due to arthritis.
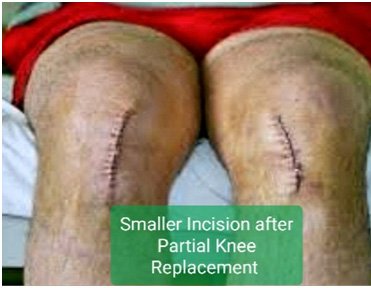
surgery done in patients having single compartment disease of the knee. In partial knee replacement we resurface the affected compartment with metallic implant thus curing the pain of the patient.
Everyone among us once in a while experience this Popping and Crackling sounds from our knees. For some it is once in a while but for others it is quite frequent and bothersome. In this article I will try to explain you about the common causes behind this sound produced by your knees and when to seek medical advice.
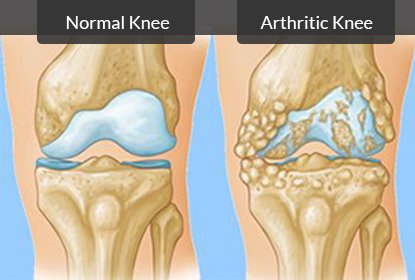
Erosion of the cartilage and bones of our knee leads to abnormal grinding of the structures of our knee which leads to the production of Crackling sound on the movements of our knee. This sound is almost always associated with pain in your knees and is one the early symptoms of Knee Arthritis.

This may lead to damage to the structures of the knee like Meniscus(Cushion) or knee cap or ligaments and bones which may be the underlying cause of abnormal sounds produced by your knee. This may be associated with pain, laxity or locking of knee depending on the structure involved.
With due course of time, small gas filled bubbles can build up in the Synovial fluid. When you move your knees some of these Gas Bubbles may burst producing Crackling sounds. This is usually not associated with pain and is harmless.
These are the structures which hold your joints in place. Sometimes due to degenerative changes in the bones small bony bumps appear at the edges of knee bones. And on movement of knee these ligaments and tendons snap over these bony bumps and produce clicking sounds. They may or may not be associated with pain.
When your Knee Cap doesn't move in the described path with the movement of knee then this may lead to production of abnormal sounds. This condition may be present since birth or due to age, injury or life events.
After Total Knee Replacement your damaged bone surface is replaced by metals and plastic. These are much harder structures than bones and cartilage. Thus on movement of your knees these artificial components of knee replacement produce sounds. This is a very common phenomenon after surgery and shouldn't be worried upon.
Osteoarthritis of knee is a very common problem in old age. But all knee arthritis doesn't require Knee Replacement. Their are multiple options available which can provide moderate to good pain relief in early Osteoarthritis of your knee. Here I will be telling you few of that options.
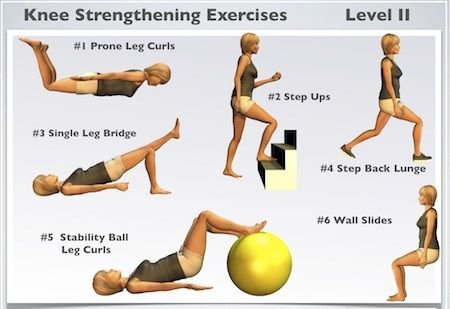
This is the mainstay of conservative treatment in a patient with knee arthritis. A good strong muscles around your knee, greatly off loads your knee and also reduces muscle spasm, thus giving good pain relief. Follow the link to learn exercises for knee arthritis:

Researches show that every 4.5 kg gain in weight increses the chances of knee arthritis by 35%, and on the other hand lossing 4.5 kg of weight reduces 4 times pressure over your knee. Try to keep your BMI less than 25.
This has shown to delay your progression of knee arthritis and also moderate pain relief. But is effective in Stage 1 or early stage 2 of Arthritis
This has shown to provide some relief when injected in the knee, but long term studies to this is still awaited.
In this procedure your Geniculate nerves(nerves which supply the knee joint) is ablated by Cold Frequency Ablator. This reduces your Knee pain but has no role in rectifying the disease. Adviced only in those how are not physically fit for Knee replacement surgery.
Limited role, not very cost effective. Provide pain relief for shorter duration and has no role in modifying the disease process.
Surgery done in partially damaged knee. Provide very good result and also correct the deformity. Delays the progression of knee Arthritis.
Their are multiple walking aids available in the market. They off- loads your knee and provide some stability. Few good ones are very expensive.
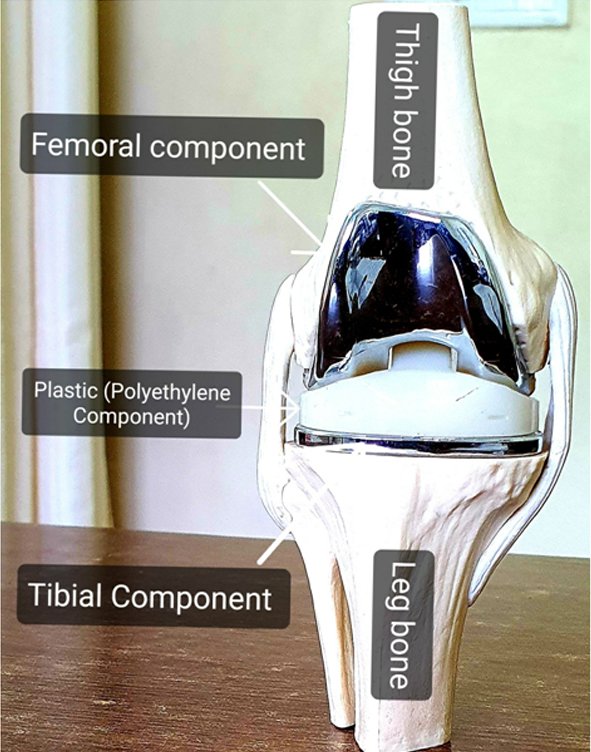
Here I will be explaining you only about the implants used in Primary Total Knee Replacement.
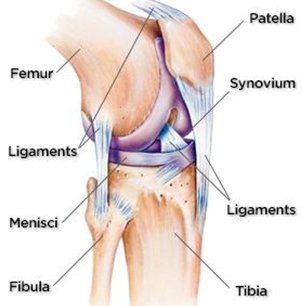
The model below is showing the different components in Knee Replacement:

Fig.1 :Knee model seen from front.
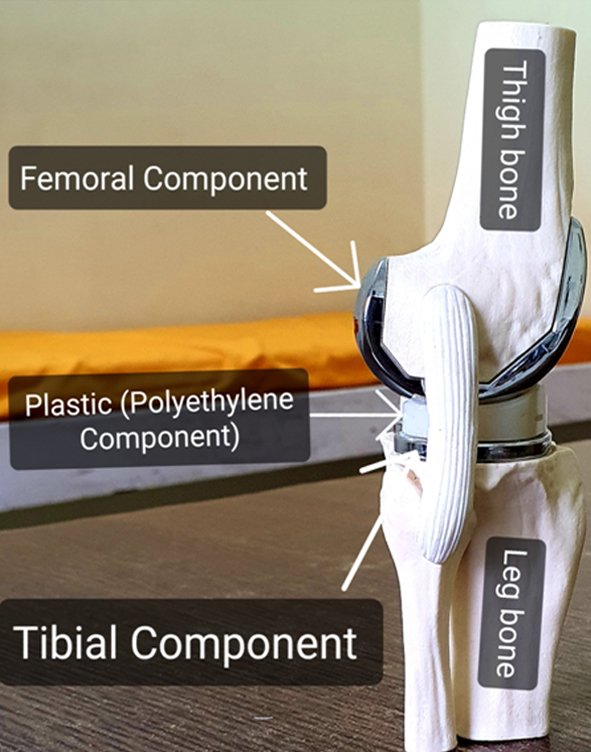
Fig 2: Knee Model seen from side
Your surgeon in his basket has variety of implant types and the one to be used in you depends on lots of factors like:
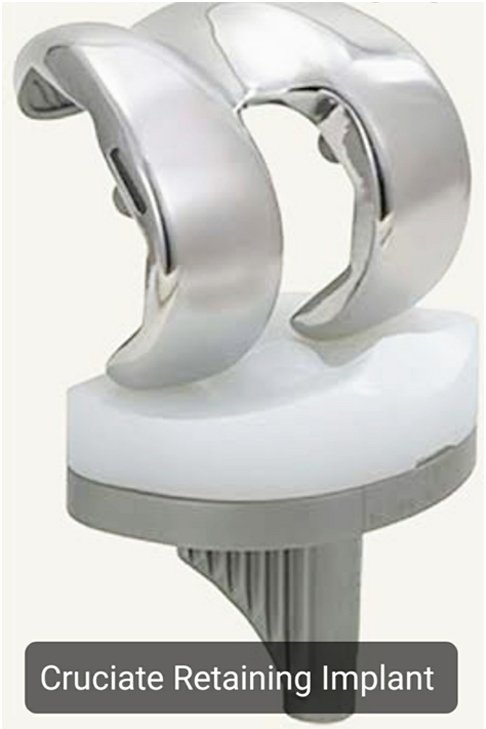
Plastic Component is Fixed to the tibial Component. This implant is also called as Fixed Bearing implants.
Plastic Component is Rotating on the tibial component. This is also known as Rotating Platform implant
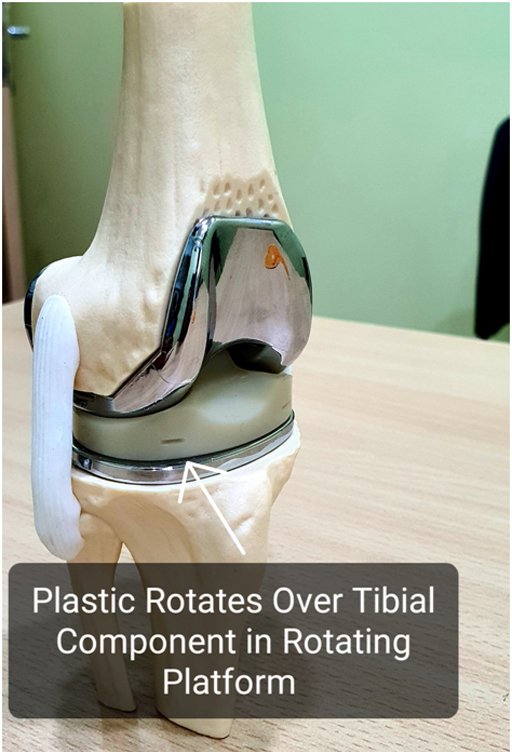
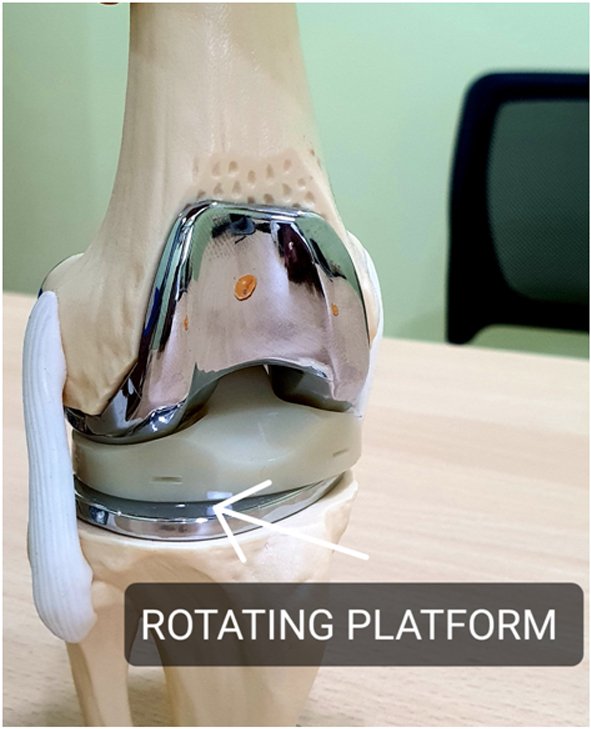
Figure showing Rotation in Rotating platform implant


in bed or floor

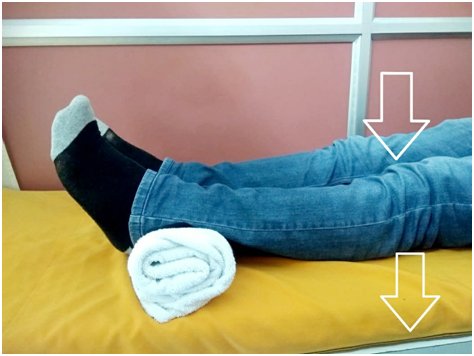
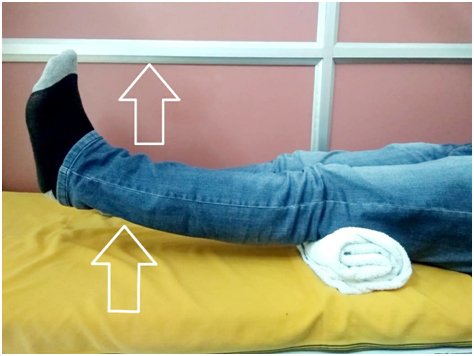

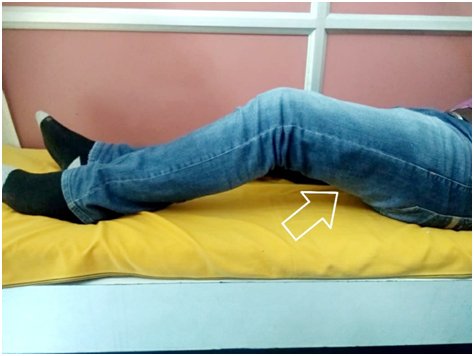
In a chair or on a firm couch
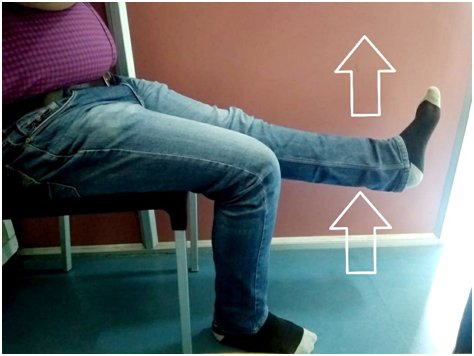
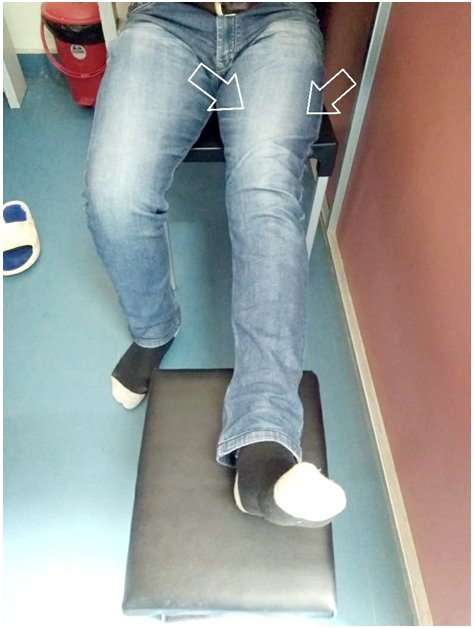
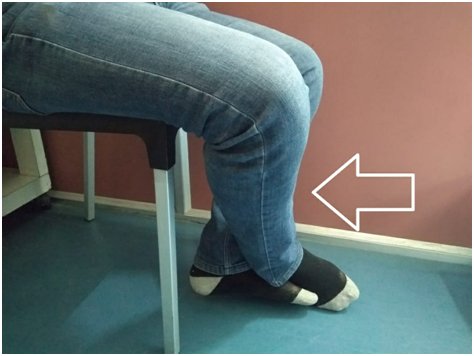

Hold onto a supportive surface
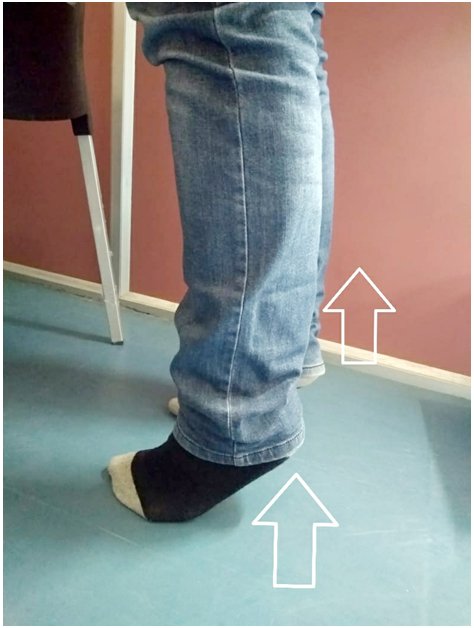
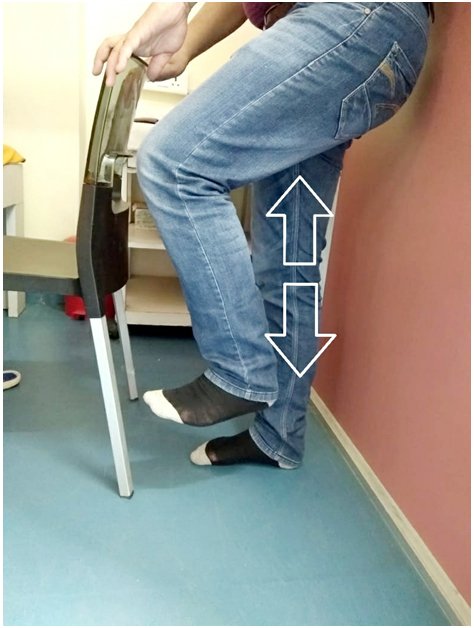
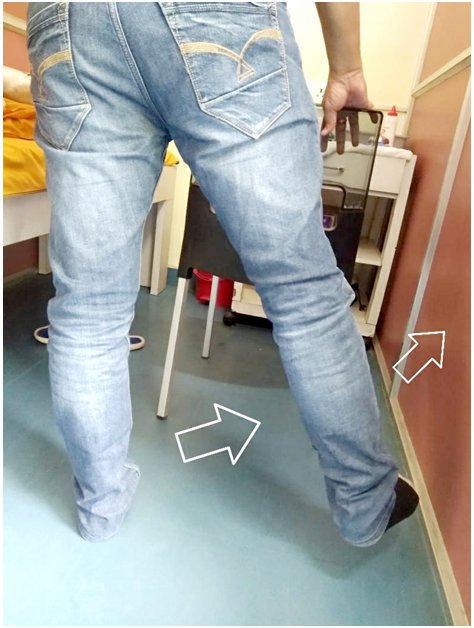

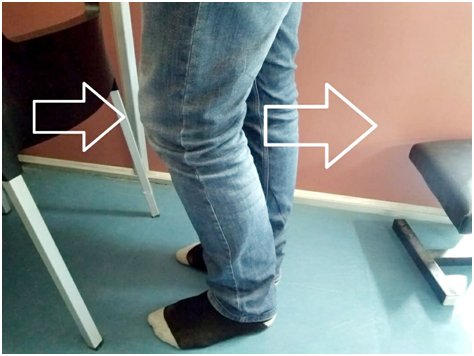

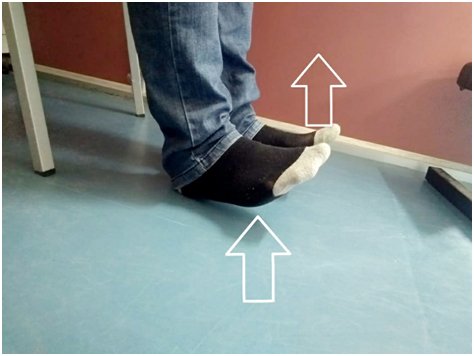



Important: All patients should do their exercises as per thier Knee Surgeon advice. Feel free to write to me your questions and feedbacks as they are my driving forces...
In my previous article I tried to inform you on "WHEN SHOULD I HAVE MY KNEE REPLACED". THE MORE IGNORANT WE STAY THE MORE IS THE ANXIETY WE FACE.
In this article I will again address a very common query and anxiety in my patient that what is the timeline of recovery after my knee replacement surgery.
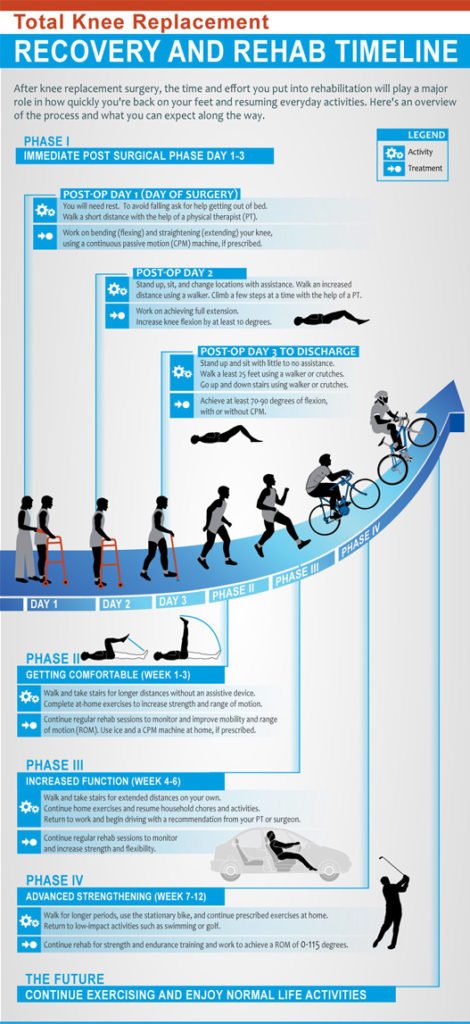
Common questions asked by patients regarding recovery period is:
Many such questions are asked by patients regarding their recovery.
So lets know, what you are going to experience in different timeline from your knee replacement surgery.
3. KNEE REPLACEMENT SUPPORT SYSTEM:

1. Period Early after Surgery:
Ice Packs and Elevation:
4. Your knee will be typically be swollen immediately after surgery and this is quite a common issue to all the patients. The best thing which you can do to reduce the discomfort is to apply ICE and ELEVATE the knee.
5. I recommend my patients a Larger Ice Packs that can drape over the knee. Readymade ice packs are readily available but those who don't find adequate size, for them it is extremely easy to make your own Ice packs.
Lets learn how to make your own ice packs.

The advantage of this pack is that it can be easily moulded around your knees.Ice packs should be used frequently while your knee is swollen.
2. Recovery during first 6 weeks:
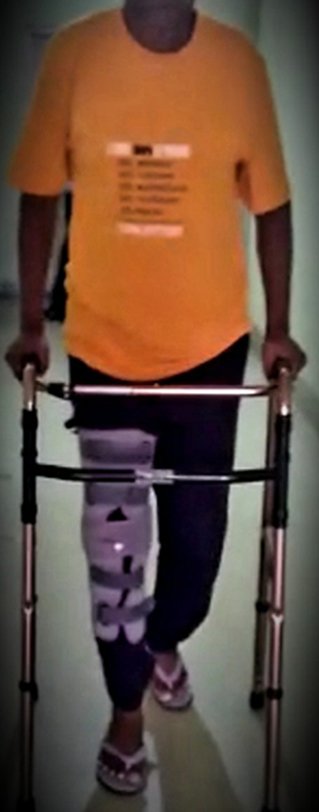
Patient ambulating early after surgery
Common issues in first 6 weeks:
#Solution:A good night sleep returns over time. Check with your Physian for any pills needed for sound sleep. Apply braces during sleep to avoid abnormal positioning of knee during sleep and also avoid flexion contractures of knee.
#Traveling during the first 3 weeks after surgery should be restricted
3. Recovery from 6 to 12 weeks:
" Moons and years passes by and are gone forever but a beautiful moment shimmers through life a ray of light".

4. Recovery after 12 weeks:
" The greener side of the world is awaiting you".

# Friends feel free to put your queries on my emails, Twitter or WhatsApp.
- A Surgeon Perspective
This is a very frequent query from my patients in my OPD. Sometimes the answer is straight forward but very oftenly it requires a thoughtful analysis involving multiple intricacies.
Lets do some logical deductions:
Point 1: Your quality of life is severly affected by your knee arthritis and you have tried all conservative methods for sufficient time(pain killers, injection, physiotherapy, braces) to get relief but all went in vain.
Point 2: After evaluation of your xrays and other clinical test by your Knee surgeon you had been diagnosed to have advance knee Arthritis.
So That's it! If you fulfill both point 1 and point 2 then its time to go for Knee Replacement. Right?
Yes for many patients these are the two ruling factors. However for many it is much more complex and requires brain storming analysis.
So know you known that 1+2 is not equal to Knee Replacement in every patient.
Lets take a tour of decision making from a Surgeon perspective:
Thus many patients coming to me is not an ideal patient because of multiple different problems like diabetes, stroke, chronic kidney disease, chronic liver disease, heart attack, morbid obesity other joints damaged, chronic low back pain etc etc...
The answer to these questions is somtime very complex to find but if our approach is methodical and scientific it is not impossible to reach a conclusion
I explain you with example:
1.Suppose a patient with advance Knee Arthritis leading to severe compromise in day to day activities, is having obesity(BMI >30) and uncontrolled diabetes with stenting done for heart problem, age something between 60 years to 70 years can we do knee Replacement in this patient?
2.One more example: A patient with advanced knee Arthritis with chronic low back pain(due to sever secondary degenerative lumbar spine) and multiple joint pain age 55 years to 70 years, should we operate?
Thus as a patient you must consider the following:
Feel free to write to me as I know their are many more you want to know.